I have a couple of autoimmune disorders relating to gluten, Coeliac and Herpetiformis. My pancreas is also unable to produce enough insulin, despite having normal insulin sensitivity. I came across several research papers that cite gluten as a possible trigger for chronic inflammation as well as autoimmune disorders, not just Coeliac disease. Recently, gluten has come up a few times on threads here. So here are several research papers that maybe of interest. I have done a very brief summary.
Gluten is found in grains such as wheat, barley, rye and often oats, the latter due to x contamination. Gluten is made up of peptides, glutenin and gliadin. You will find gluten in so many foods, not just the obvious ones like bread, pastries, pasta, beer and sauces, but in unexpected food groups, like egg noodles, corn flakes, soups, french fries, soy sauce and restaurant eggs. Just look at the ingredient lists in foods on the supermarket shelves, wheat is often named in bold. Gluten adds an element of elasticity to food, it is a binder making foods like breads become fluffy, and light. Without gluten bread tends to be ‘cakey’ in consistency and rather unpleasant. You can actually buy gluten as an additive.
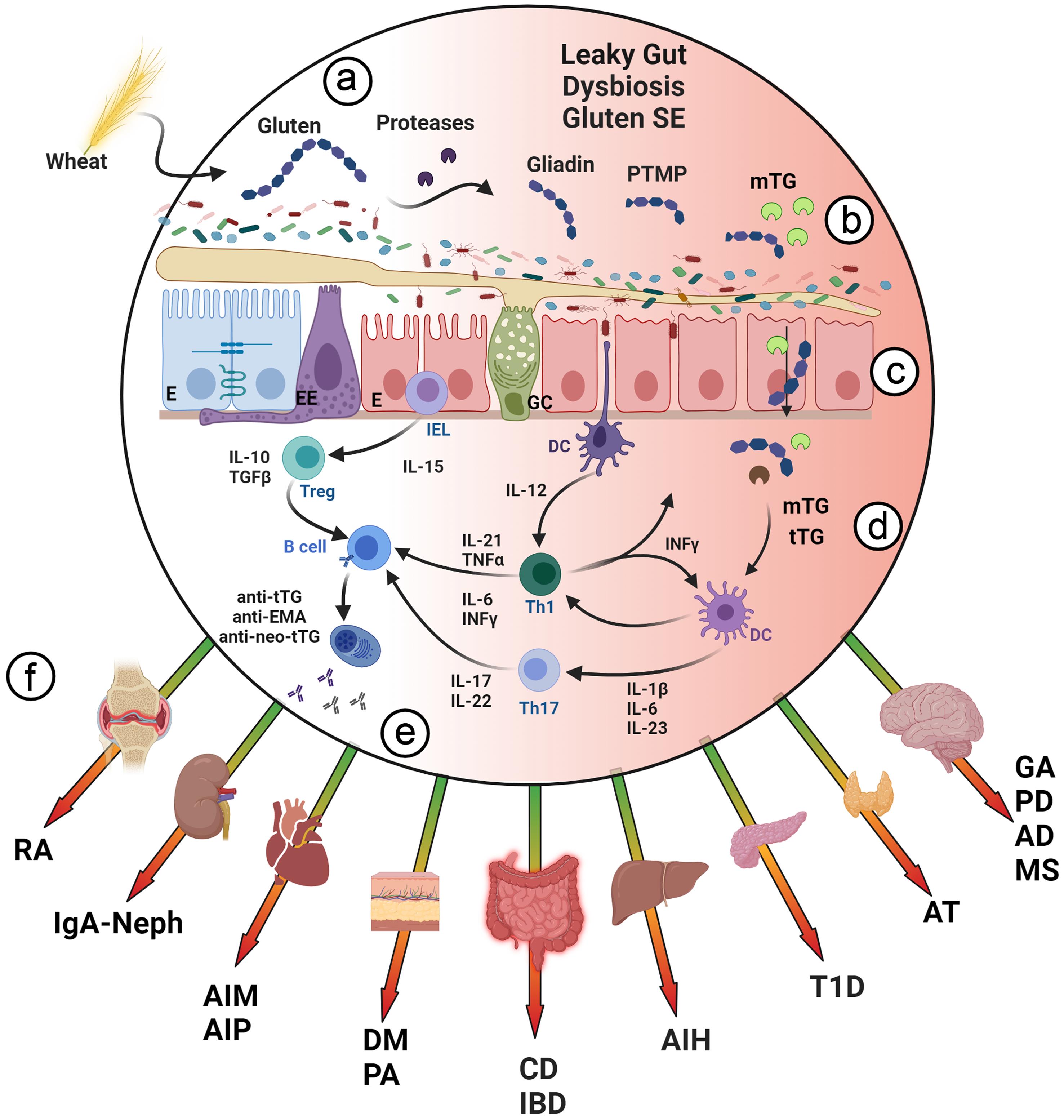
There are several things of note around gluten. Gluten is known to trigger inflammation in the body, not just in HLA DQ2 and DQ8 positive individuals. It interacts with the immune system in the gut. Gluten is also difficult to digest because of its peptides - glutenin and gliadin, gliadin making up 70% of the proteins in gluten. Gliadin is known to induce cell stress in the gut lining. This causes localized inflammatory response in the gut, IBS and GERD spring to mind. What gluten does is stretch the cells in the lining of the gut. This can make the gut lining more permeable allowing foreign molecules to enter the bloodstream and circulate around the body causing inflammation throughout the body including organs. The body responds to these foreign molecules with an immune response and the release of inflammatory molecules. It stimulates an immune response - an immunogenic effect. In other words it can stimulate the immune system which may lead to autoimmune diseases.
Parts of the body where these peptides have been found include the brain (Gluten Ataxia). In fact research has shown that gluten peptides may be a contributing factor in neurodegeneration, and chronic brain inflammation diseases. The thyroid gland (Hashimoto’s thyroiditis due to the gut-thyroid axis. The skin, herpetiformis a dermatological disruption, which I have. I also over produce histamines which may be another autoimmune response to gluten; and of course the pancreas (Type 1 DM) where gluten peptides have been found in the pancreatic islets, which apparently enhance beta-cell activity ‘increasing the expression of beta-cell antigens, and resulting in pancreatic autoimmunity’. Gluten peptides have also been found in the kidneys, the liver, and the heart.
I have attached the research papers which go into far great detail than my brief summary, but broadly speaking the immunogenic potential of gluten underscores its role as a universal trigger of inflammation and autoimmunity and not just Coeliac disease. These studies show that gluten is not just a concern for coeliacs but for everyone.

 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Gluten is found in grains such as wheat, barley, rye and often oats, the latter due to x contamination. Gluten is made up of peptides, glutenin and gliadin. You will find gluten in so many foods, not just the obvious ones like bread, pastries, pasta, beer and sauces, but in unexpected food groups, like egg noodles, corn flakes, soups, french fries, soy sauce and restaurant eggs. Just look at the ingredient lists in foods on the supermarket shelves, wheat is often named in bold. Gluten adds an element of elasticity to food, it is a binder making foods like breads become fluffy, and light. Without gluten bread tends to be ‘cakey’ in consistency and rather unpleasant. You can actually buy gluten as an additive.
There are several things of note around gluten. Gluten is known to trigger inflammation in the body, not just in HLA DQ2 and DQ8 positive individuals. It interacts with the immune system in the gut. Gluten is also difficult to digest because of its peptides - glutenin and gliadin, gliadin making up 70% of the proteins in gluten. Gliadin is known to induce cell stress in the gut lining. This causes localized inflammatory response in the gut, IBS and GERD spring to mind. What gluten does is stretch the cells in the lining of the gut. This can make the gut lining more permeable allowing foreign molecules to enter the bloodstream and circulate around the body causing inflammation throughout the body including organs. The body responds to these foreign molecules with an immune response and the release of inflammatory molecules. It stimulates an immune response - an immunogenic effect. In other words it can stimulate the immune system which may lead to autoimmune diseases.
Parts of the body where these peptides have been found include the brain (Gluten Ataxia). In fact research has shown that gluten peptides may be a contributing factor in neurodegeneration, and chronic brain inflammation diseases. The thyroid gland (Hashimoto’s thyroiditis due to the gut-thyroid axis. The skin, herpetiformis a dermatological disruption, which I have. I also over produce histamines which may be another autoimmune response to gluten; and of course the pancreas (Type 1 DM) where gluten peptides have been found in the pancreatic islets, which apparently enhance beta-cell activity ‘increasing the expression of beta-cell antigens, and resulting in pancreatic autoimmunity’. Gluten peptides have also been found in the kidneys, the liver, and the heart.
I have attached the research papers which go into far great detail than my brief summary, but broadly speaking the immunogenic potential of gluten underscores its role as a universal trigger of inflammation and autoimmunity and not just Coeliac disease. These studies show that gluten is not just a concern for coeliacs but for everyone.

Gluten is a Proinflammatory Inducer of Autoimmunity
Gluten has multiple harmful effects that compromise human health, not only in gluten-dependent diseases but also in non-gluten-affected chronic inflammatory conditions. After consumption, the indigestible gluten peptides are modified by luminal microbial transglutaminase or transported through...
www.xiahepublishing.com

Possible Prevention of Diabetes with a Gluten-Free Diet
Gluten seems a potentially important determinant in type 1 diabetes (T1D) and type 2 diabetes (T2D). Intake of gluten, a major component of wheat, rye, and barley, affects the microbiota and increases the intestinal permeability. Moreover, studies have ...
