|
|
|
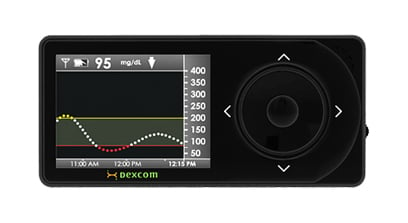
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) is a relatively new method of checking and controlling glucose levels in patients with diabetes.
CGM systems differ from traditional blood glucose testing as they automatically monitor the amount of glucose in the body's interstitial fluid - not the bloodstream - 24 hours a day, thus providing more data about how your glucose levels vary through the day and night, for example after a meal, when you exercise, or while you are sleeping.
For those who find it hard to regulate glucose levels, this additional real-time information can make the difference in enabling them to take control of their diabetes.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current CGM systems are intended only as an additional tool to traditional blood glucose testing.
Attitudes to blood glucose testing can vary quite considerably and it is widely regarded as a must for people with insulin-dependent diabetes only.
However, studies have shown it can be of benefit for individuals with type 2 diabetes who are not treated with insulin.
If you are interested in self-monitoring your blood sugars but have questions about testing, you should be able to find the answers you are looking for in our blood glucose testing FAQs.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interested in CGM? To help you decide whether it is a suitable option, read what members of our online community have to say about their experiences of continuous glucose monitoring. |
|
|
|
|
|
