Blood glucose testing, also known as blood glucose monitoring, is one of the main tools involved in controlling diabetes.
Not everyone with diabetes will test their blood glucose levels but it is regarded as being very beneficial for helping to make diet and medication dosing decisions.
If you are on any medication that can lead to hypoglycemia (most notably insulin), you should test your blood glucose levels.
What is blood glucose testing?
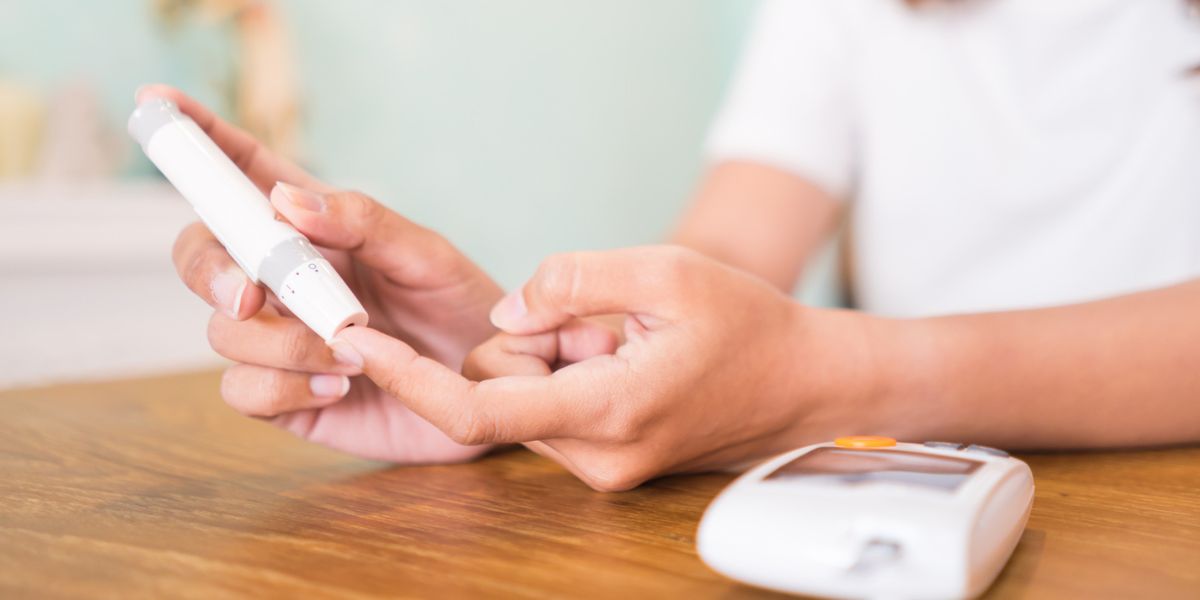
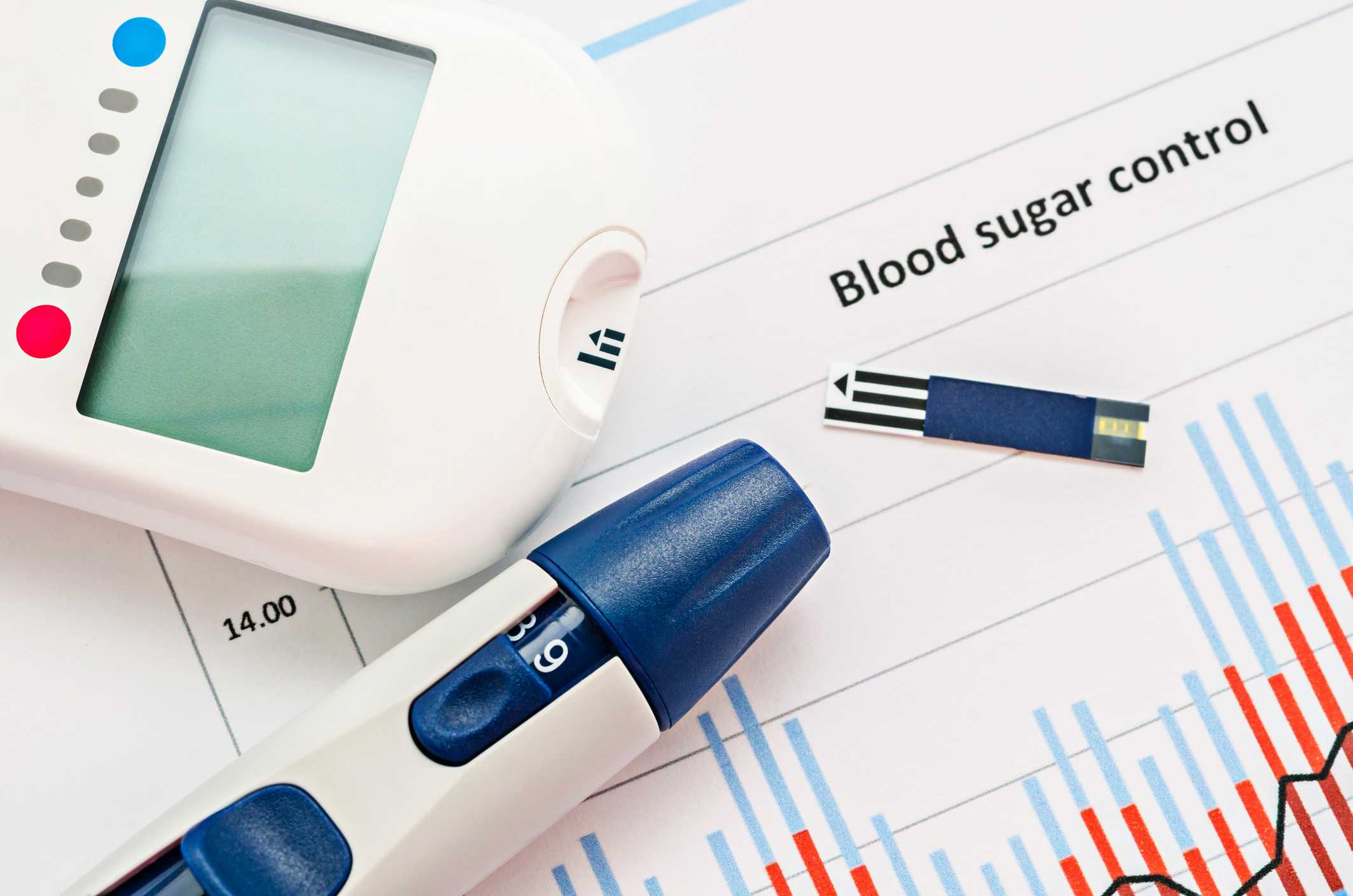
Blood glucose testing is the process used to measure the concentration of glucose in your blood. Blood glucose testing can be carried out at home using a blood glucose meter
A blood test involves pricking your finger with a small needle called a lancet, drawing a drop of blood from the finger and applying it to a test strip that has been engaged into a blood glucose meter.
Guides:
How does blood glucose testing help to control diabetes?
Blood glucose testing can help to control diabetes in a number of ways:
- Informing food choices and portion quantities
- Assisting medication dosing decisions
- Identifying periods of high or low blood glucose levels
In turn, this can lead to:
- A reduction in HbA1c (improved long-term glycemic control)
- A lower risk of serious diabetic complications
- Reduced depressive symptoms
- Improved confidence in self-management of diabetes
What are the disadvantages of blood glucose testing?
Disadvantages of blood glucose testing may include:
- Pain when pricking fingers
- Cost of blood glucose testing supplies – if these need to be self-funded
- Anxiety if no education has been provided on how to interpret and act on the glucose results
Who is blood glucose testing suitable for?
Many people with diabetes benefit from blood glucose testing if they are provided with education on how to interpret their results and take appropriate action to improve their control.
All people who take insulin should regularly test their blood glucose levels and people on certain tablets, such as sulfonylureas, should also test their blood glucose levels to identify any periods of low blood glucose levels.
People on other medications that do not cause hypoglycemia may not need to test their blood glucose levels, however, many people will wish to check their blood sugar levels in order to help them make decisions to maintain and improve their diabetes control
Should I test my blood glucose levels?
Attitudes to blood glucose testing can vary quite considerably. Some people with diabetes, particularly those that have not received any education on managing their diabetes, find that blood glucose testing is not helpful and only contributes to anxiety.
However, other people, particularly those that are aware of how to interpret results and take appropriate action, find blood glucose testing to be vital to their diabetes management
Some people with type 2 diabetes on non-insulin medication regimes may find it difficult to be prescribed blood glucose testing equipment.
For more on this issue, see availability of blood glucose test strips.
How often do I need to do blood tests?
How often you should test your blood glucose can vary depending on your type of diabetes.
People with type 1 diabetes should test at least 4 times per day including before each meal and before bed.
People with type 1 diabetes should also be supported by their GP to test up to 10 times a day (and more often in some cases) if factors apply such as taking part in sport, to ensure safe driving and if you have impaired hypo awareness.
People with other types of diabetes on hypo-causing medication should test their blood glucose levels at least once a day. Aim to test at different times of the day to discover whether blood glucose levels are going too low (or too high) at certain times of day. This will help you to take steps to prevent low or high results from happening and this can be done with help from your doctor.
If on medication that can cause hypos, be prepared to test your blood glucose levels at any time you feel the signs of hypoglycemia
- For more information, see how often should I test my blood?