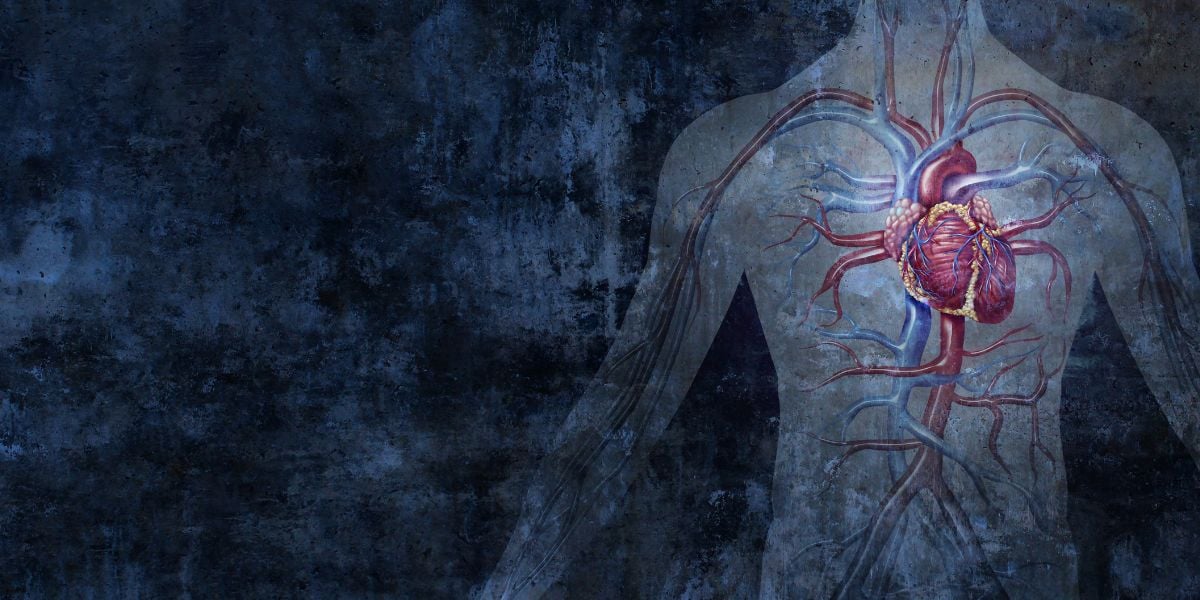
The circulatory system is responsible for the delivery of blood, and therefore glucose in the blood, round the body.
The different complications of diabetes are a consequence of damage to blood vessels in different parts of the circulatory system.
What is the circulatory system?
The circulatory system is essentially the body infrastructure, providing the route ways for the blood to transport oxygen, nutrients and hormones to and from the cells and organs.
The heart plays a key role in the circulatory system, helping to pump blood around all the body.
Blood vessels range in size, from larger arteries into very small blood vessels called capillaries.
Capillaries feed into the veins which carry blood back to the heart.
The role of the circulatory system
The circulatory system performs a number of roles, including:
- Delivering oxygen and nutrients, including glucose, to the body’s cells
- Carrying carbon dioxide and waste products away from the cells
- Transporting hormones and therefore helping the body communicate with its organs
- Transport white blood cells to fight off infection
- Regulating body temperature
The circulatory system and diabetes
The circulatory system allows blood glucose levels to be regulated.
The hormone glucagon, carried in the blood, signals the liver to release glucose into the blood and the presence of insulin in the blood instructs the cells to take in glucose from the blood.
If blood glucose levels become too high for extended periods of time, damage can be sustained by the blood vessels.
If significant numbers of blood vessels are damaged, this can have a negative effect on the functioning of the body.
Circulatory complications in diabetes
Where damage is sustained to a significant number of blood vessels in a certain area of the body, diabetic complications will develop.
Neuropathy (nerve damage) results from damage to the blood vessels that feed the nerves. Damage to circulation and the nerves in the foot and legs can increase the risks of developing foot ulcers and could lead to amputation.
When blood vessels feeding organs are damaged, this can affect performance of the organ. When the kidneys are damaged in this way, they lose their effectiveness in filtering the blood. If the damage continues, it can lead to kidney failure.
Each of the complications in diabetes is related to damage to the circulatory system.