Mediterranean diets rich in fruit and vegetables are known to be healthy for people with diabetes.
As well as being protective against type 2 diabetes, Mediterranean diets rich in fruit, vegetables and fibre can help people with diabetes to control their blood sugar levels.
Where does the Mediterranean diet come from?
The Mediterranean diet is thought to have originated in Crete, Southern Italy and Greece.
Previous large-scale studies have linked a Mediterranean diet with a lower chance of developing diabetes.
What is in a Mediterranean diet?
A traditional Mediterranean diet is principally composed of:
- Oily fish
- Poultry
- Fresh fruit and vegetables
- Legumes
- Fresh bread
- Pasta
- Olive oil
One of the reasons why Mediterranean diets are healthy is that they include a strong vegetable content.
Vegetables such as tomatoes, peppers, aubergines, olives, onions, rocket and lettuce are not only great for blood glucose levels but make for very visually appealing meals too.
Most people should be able to include a moderate amount of fruit. If you are susceptible to sharp spikes in blood glucose levels opt for lower carb fruits such as berries.
A Mediterranean diet typically includes a good intake of fat from a diverse set of foods including feta and mozzarella cheeses, yoghurt, olive oil, avocado, oily fish and nuts.
Beans nuts, seeds, eggs, poultry and a moderate amount of red meat provide protein.
Pasta and bread, which would ideally be freshly made, provide carbohydrate in addition to starchy vegetables.
Not everyone with diabetes can handle starchy foods as well as others so stick to portion sizes that won’t greatly raise your sugar levels.
You do not need to stick to just having Mediterranean dishes but should embrace the spirit of the diet which is to focus on fresh rather than processed foods.
Why is the Mediterranean diet recommended?
The diet is often recommended by health charities and the NHS because it has a higher proportion of unsaturated to saturated fats, includes plenty of fresh vegetables and depends on largely unprocessed foods.
The diet is not a restrictive diet and so it is not linked with vitamin or mineral deficiencies and therefore gets further praise as an easy diet to adopt and follow.
What are the health benefits of the Mediterranean diet?
The Mediterranean diet has been show, particularly in combination with regular exercise, to promote good heart health and is associated with a lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes and cancer.
Mediterranean meal plan
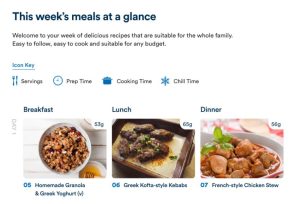
If you’re looking to start a Mediterranean diet, download our free meal plan to get you started.
Each day is filled with delicious, nutritionist-approved recipes complete with full nutritional breakdowns and vibrant photos.
To access the meal plan, you require a free Diabetes.co.uk account.
Which large studies have tested the relationship between the Mediterranean diet and diabetes?
A study involving 14,000 Spanish people scored people on factors within the Mediterranean diet.
The participants were ranked into three groups, each of which was found to have a different risk of diabetes.
However, the study was criticised for the group being too young and more rigorous studies were advised.
That said, a number of studies have recently shown the benefits of a Mediterranean diet:
- Mediterranean diet helps symptoms of depression in young men new research finds
- Mediterranean diet can help improve sleep quality
- Adopting a Mediterranean diet improves fertility, evidence suggests
- Mediterranean lifestyle reduces cancer mortality risk
- Mediterranean lifestyle lowers risks of premature death and cancer
- Mediterranean diet and keeping active could reduce risk of hospital-associated disability in older people
The Mediterranean diet stands out as a sustainable and beneficial approach to eating.
Whether you’re looking to reduce your risk of chronic diseases, manage your weight, or simply enjoy a healthier lifestyle, the Mediterranean diet may just be the right choice for you.
As always, speak to your doctor before making any significant changes to your diet.







