A busy social life, sports and work at school, blossoming relationships and dealing with your parents are all things that teenagers have to cope with.
Having diabetes on top can make things more difficult, and regular diabetes testing is the key to keep the risk of developing complications down and the energy levels up.
Avoiding diabetes complications as a teenager using regular testing
Taking control of diabetes and establishing an effective routine is the key to cutting down the risk of diabetic complications. Controlling your blood glucose levels automatically means a decrease in the risk of developing diabetes complications.
Keeping levels at the average level for as long as possible is the key.
Pre-prandial (before meals) readings should stand between 4-6mmmol/L , whilst post-prandial (two hours following a meal) readings should be 10mmmol/L
These figures are intended as a basic guide rather than numbers to be strictly adhered to.
What should I do if my blood sugar climbs above 10mmmol/l?
Unfortunately for diabetic young people, and those who are newly diagnosed, tests can be confusing without being dangerous.
Tests can sometimes yield a surprisingly high or low result, and although these should always be treated with caution, a single high or low result is not always a cause for panic.
Instead, diabetes experts advise keeping an even closer eye than usual on your blood glucose levels.
Regular diabetes testing as a teenager
Wherever you are and whatever you are doing, keeping your testing regular allows you to have the greatest level of control over your diabetes possible.
This can seem, literally, painful. Having to interrupt a busy day, or a fun occasio, just to test the blood can be easy to ignore, especially when the results seem to be similar all the time anyway.
There is nothing wrong with being confident when it comes to testing for diabetes, but thinking that you can feel your blood glucose levels is not always entirely accurate.
Diabetes experts advise teenagers to keep a close monitor using test strips and a meter. Particularly important testing times include early in the morning, before and after physical activity (of whatever type), before and after meals, and if you feel unwell at any time.
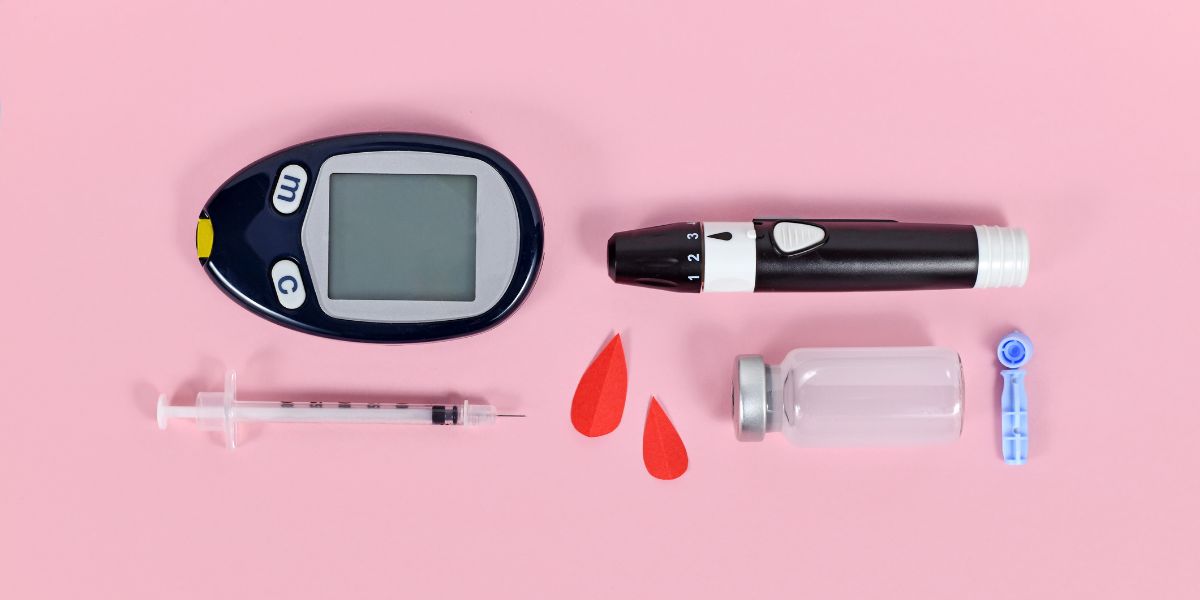
What does a blood glucose monitor do?
As a diabetic teenager, your healthcare team should have shown you how to use a blood glucose meter.
When you test your blood using a meter, the result will display how much glucose is in your blood.
The meter reads off your results by combining your blood (by pricking your finger) with a test strip.
Meters and test strips from a reputed provider are completely accurate, providing the equipment is properly looked after and test is correctly carried out.
Looking after diabetes testing kit
Looking after diabetes testing kit is essential, and if you feel that your kit is in any way damaged or inaccurate it should be replaced immediately.
Exposing a blood glucose meter or testing strips to direct sunlight or intense cold is also a bad idea.